KMG-BACKSTOR-01
The server sits outside the domain for security reasons, so as to not get infected if the Domain is infested.
Purpose
KMG-BACKSTOR-01 is the main Backup Server Repository for our Veeam Backups. This server functions as a backup repository for Veeam, providing storage for backup data managed by KMG-VEEAM-02.
Accessibility
The server is located in the main server room(Rack C) and can be remotely managed using iLO Advanced firmware version 3.01 with an IP address of 10.222.222.51.
Operating System
The server operates on Microsoft Windows Server 2019 Datacenter 10.0.17763.
Hardware
The server is a Proliant DL380 Gen10 with the following specifications:
- Processor: Intel(R) Xeon(R) Silver 4214 CPU @ 2.20GHz
- RAM: 64GB Advanced ECC @ 2400MHz
- HDD: 109.14TB (RAID 6), along with 136.7GiB of RAID 1 storage
- Network Adapter: HPE Ethernet 1Gb 4-port 331i Adapter + Network controller in PCI-E Slot 1 connected to 10GB-LACP logical network adapter.
Storage
Storage Utilization and ReFS Filesystem Behavior
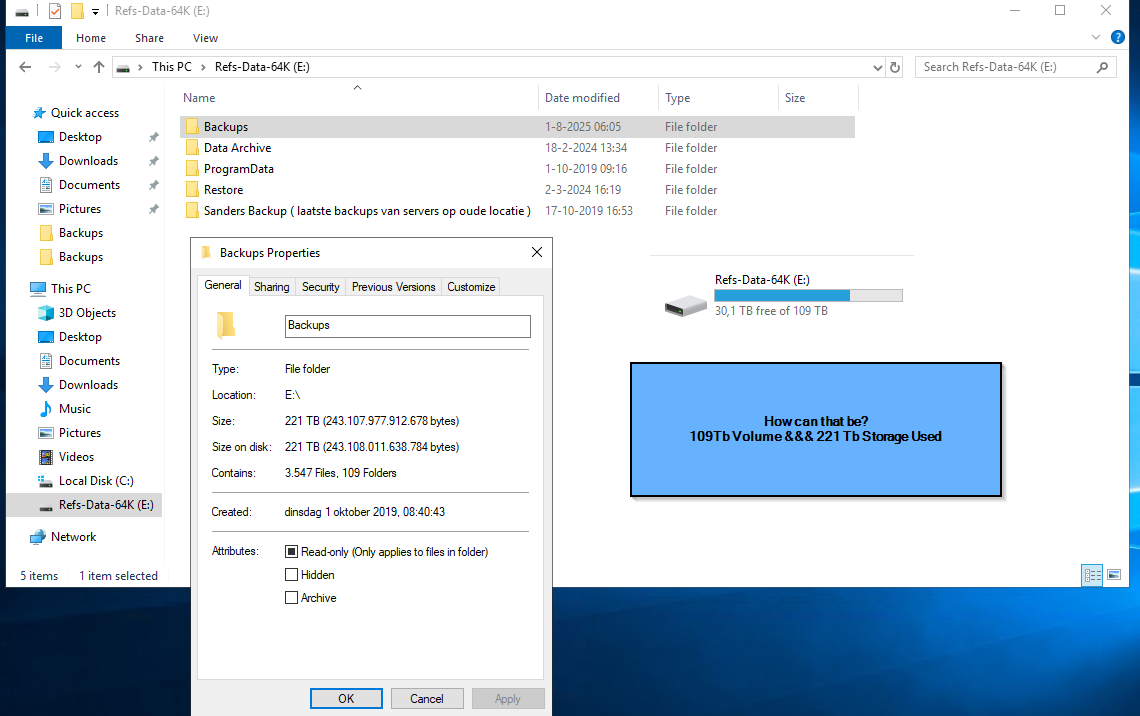
- The "ReFs-Data-64K (E:)" volume shows a total capacity of 109 TB, but the "Backups" folder alone reports a size of 221 TB, with the same value for "size on disk." The drive has 30.1 TB free of 109 TB, and the "Backups" folder contains 3,547 files and 109 folders.
- This apparent paradox is due to the use of the ReFS (Resilient File System) with block-level deduplication and copy-on-write features. ReFS allows the logical size of stored data to exceed the physical volume size, thanks to advanced deduplication and pointer-based storage mechanisms.
Expert Discussion: ReFS, Veeam, and Backup Efficiency
- ReFS is a copy-on-write filesystem with block deduplication. When a full backup is made and only a small portion of data has changed, only the changed blocks are written; unchanged blocks are referenced via pointers.
- Veeam Backup & Replication can leverage these ReFS features, resulting in highly efficient storage usage for synthetic full backups. Veeam is one of the few backup tools that can fully utilize ReFS's block-level tricks.
- Changed Block Tracking (CBT) is used to identify only changed blocks from VMware for backup. On traditional filesystems, a synthetic full backup would reconstruct all data, but on ReFS, block duplication means the new "full" is mostly pointers to unchanged blocks. The result is a "synthetic of the synthetic"—a full backup that is not a true full copy, but a construct using deduplication and pointers.
Legacy Data and Storage Hygiene
- The folder "Sanders Backup (laatste backups van servers op oude locatie)" is present on the same E: volume, with a size of 3.20 TB, containing 81 files and 6 folders, created on 17 October 2019.
- A highlighted note in the image asks: "Sanders Backup - is it still necessary????" This folder appears to be a legacy backup from a previous server/location, and its continued presence may be consuming valuable storage. A review is needed to determine if this data is still required.
Synthesis and Recommendations
- ReFS with Veeam enables highly efficient backup storage, allowing logical backup sizes to far exceed physical disk capacity through deduplication and pointer-based storage.
- Storage reporting in Windows may show confusing or seemingly impossible figures due to these advanced filesystem features.
- Legacy data (e.g., "Sanders Backup") should be periodically reviewed to ensure storage is used efficiently and only for necessary data.
Recommendations:
- Educate stakeholders about ReFS and Veeam's deduplication to prevent confusion over storage usage reports.
- Regularly review legacy backup folders to determine if they are still needed, and archive or delete as appropriate.
- Monitor free space on the ReFS volume to ensure that deduplication and pointer-based storage do not lead to unexpected out-of-space errors.
- Document backup and storage policies to clarify how logical and physical storage are managed, especially for compliance and disaster recovery planning.
Network Information
The server has a connection with the local network via adapter 1 (HPE Ethernet 1Gb 4-port 331i Adapter - NIC) and adapter 2 (Network Controller in PCI-E Slot 1) with the IP address of 10.222.2.180. The server uses a 10GB-LACP logical network adapter for network communication.
Network Interface Overview
| Interface | IP Address | Subnet Mask | Gateway | MAC Address(s) | Switch | Port/Trunk | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4-port 1Gb Ethernet Adapter | — | — | — | 08:F1:EA:F4:48:3C, 08:F1:EA:F4:48:3D, 08:F1:EA:F4:48:3E, 08:F1:EA:F4:48:3F | — | — | HPE Ethernet 1Gb 4-port 331i Adapter |
| NIC Team (Fiber) | 10.222.2.180 | /22 | 10.222.0.2 | 74:46:A0:72:EF:94, 74:46:A0:72:EF:95 | Aruba-Stack-3810M | Trk41 (1/A2,2/A2) | 10GB-LACP logical network adapter (NIC4+NIC5, Windows Team) |
| Dedicated iLO | 10.222.222.51 | /24 | 10.222.222.1 | 08:F1:EA:F4:48:3A | Aruba-Stack-3810M | 1/40 | iLO Advanced firmware v3.01 |
Network Connectivity Diagram
Monitoring
Monitoring and alerting for this server is primarily handled via SNMP and iLO AlertMail, ensuring that the IT team is promptly notified of critical events and system health issues. This section outlines the key monitoring configurations in place.
SNMP Alerts
-
SNMP Status: Enabled
-
SNMP Port: 161
-
Read Community 1:
fC5Ix1 -
SNMPv3 Users:
- User:
oneview_5244545661554f634d734d32- Authentication Protocol: SHA
- Privacy Protocol: AES
- Engine ID: 0x800000E804435A3239333230475734
- User:
-
SNMP Alert Destinations:
- Destination: 10.222.2.169
- Protocol: SNMPv3 Trap
- User: oneview_5244545661554f634d734d32
- Destination: 10.222.2.169
-
Trap Source Identifiers:
- iLO Hostname
- OS Hostname
- SNMPv1 Request/Trap
- SNMPv3 Request/Trap
- Cold Start Trap Broadcast
-
Periodic HSA Trap Configuration: Disabled
-
SNMPv3 Inform Retry: 2
-
SNMPv3 Inform Time Interval: 15 seconds
Email Alerting (iLO AlertMail)
- AlertMail Status: Enabled
- Recipient Email Address: ict@keesing.com
- Sender Domain/Email: kmg-backstor-01@keesing.com
- SMTP Server: smtp.keesing.com
- SMTP Port: 25
- SMTP Secure Connection (SSL/TLS): (configurable)
- SMTP Authentication: (configurable)
These monitoring and alerting mechanisms are essential for maintaining the operational health and security of the backup storage server. They ensure that the IT team is immediately informed of any issues requiring attention, as described in the Responsibility section.
Responsibility
The IT team is responsible for the operation, maintenance, and up-time of the server. They perform daily checks to ensure backups are being correctly executed and there is sufficient storage space for new backups.